Established - c. 1070 BC
Disestablished - c. 550 AD
Ancient Nubian cultures were sophisticated and cosmopolitan, as the region served as a major trading center for goods from the African interior, Arabian desert, and Mediterranean basin.
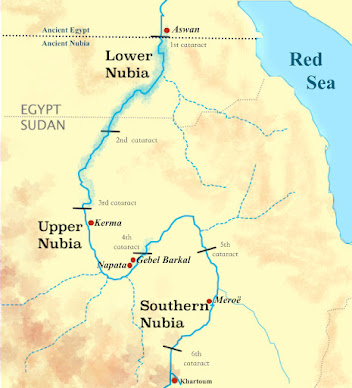
Three Kushite kingdoms dominated Nubia for more than 3,000 years, with capitals in Kerma, Napata, and Meroë.
The Kush rulers were regarded as guardians of the state religion and were responsible for maintaining the houses of the gods. Some scholars believe the economy in the Kingdom of Kush was a redistributive system.
The location of the kingdom along the Nile River provided strategic communication and trade routes both within the kingdom and throughout northeastern Africa. Kushites also farmed the Nile River valley, relying on irrigation systems and rainfall in some areas.
The Nubian kingdom of Kush thrived for centuries at Meroë. Kush had its own dynastic leaders, trade systems, adaptations of Egyptian religion, and even its own alphabet and languages. From the 2nd century BC there was a separate Meroitic writing system. This was an alphabetic script with 23 signs used in a hieroglyphic form (mainly on monumental art) and in a cursive form.
The art and architecture of the Kushites reveal a sophisticated society of innovative craftsmen. Notable architecture includes stone temple complexes such as the Lion Temple at Naqa, and the steep-sided, solid pyramids found at Meroe and Jebel Barkal.
Cushites and Egyptians engaged in trade, diplomacy, and incessant conflicts resulting in a dynamic landscape of social and political interconnections and millennia of bidirectional migration. Consequently, people of Cushite origin could be found at every tier of Egyptian society—including the office of the pharaoh.
Kush became weaker as Egypt was absorbed into the Roman Empire and Rome came to dominate trade to the north. The Kushite kingdom with its capital at Meroe persisted until the 4th century AD, when it weakened and disintegrated due to internal rebellion.
Kushite states
Saturday, April 9, 2022
The top most popular articles
-
Modern Macedonia was a part of the ancient Empire of Macedonia, which partly covered territory now in southwestern Bulgaria and northern Gre...
-
By 84os, the Picts and the Scots were ruled by one king, Kenneth I MacAlpin. The people of Alba, as the kingdom was known, spoke the Gaelic...
-
Between 2300 and 2200 BC, a remarkable cultural and political phenomenon emerged in the ancient world—the Akkadian Empire. Spanning from Ana...
-
The empire was created by Alexander the Great’s general Seleucus constituted the largest Hellenistic kingdom of the successor states. Sele...
-
The Hittites first appeared in history in the 20th century BC, as inhabitants of the Anatolian plateau with city of Hattusa. Historians tra...